ADVERTISEMENT
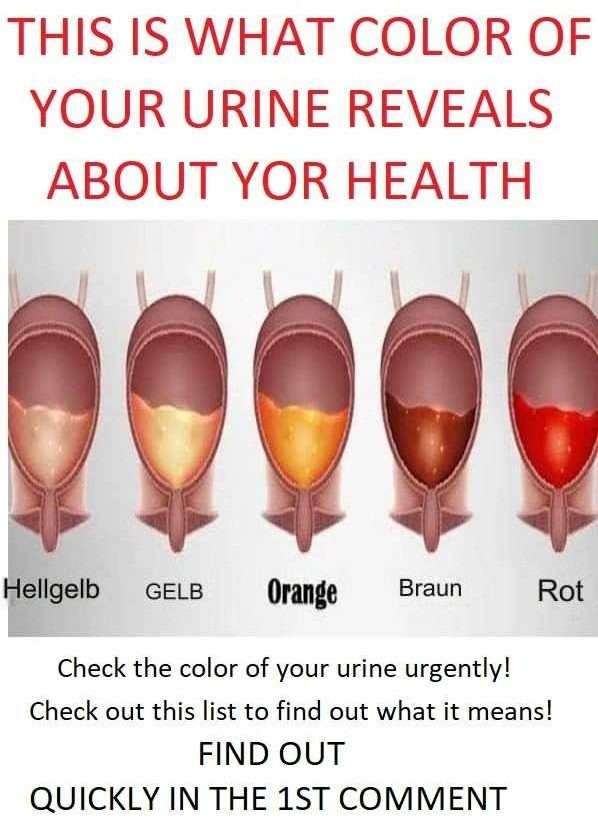
6. Pink or Red
What It Means: Possible blood in the urine (hematuria), kidney stones, infections, or dietary causes.
Explanation: Pink or red urine is often a sign of blood, known as hematuria, in the urinary tract. This can result from urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney stones, enlarged prostate in men, or, less commonly, kidney or bladder tumors. However, foods like beets, blackberries, or rhubarb can also impart a red or pink hue.
Caution: While dietary causes of red or pink urine are harmless, blood in the urine can indicate potentially serious conditions that require medical attention. If the color persists or if symptoms like pain or burning during urination, lower back pain, or fever occur, seek medical advice promptly.
7. Brown or Cola-Colored
What It Means: Possible severe dehydration, liver issues, or muscle injury.
Explanation: Brown urine can occur in cases of severe dehydration but also in situations where muscle damage has released myoglobin, a protein, into the bloodstream. This condition, known as rhabdomyolysis, places heavy stress on the kidneys. Brown urine may also be a sign of liver disease or bile duct blockages.
Caution: Brown or cola-colored urine warrants immediate attention, especially if accompanied by muscle pain, weakness, jaundice, or swelling. Rhabdomyolysis can cause kidney damage if untreated, and liver or bile duct conditions need prompt medical intervention.
8. Blue or Green
What It Means: Possible infections, medication effects, or genetic disorders.
Explanation: Blue or green urine is rare but can occur due to certain medications, dyes used in medical tests, or bacterial infections like Pseudomonas that cause green urine. A rare genetic condition called familial hypercalcemia (or “blue diaper syndrome”) can also cause blue-tinged urine.
Caution: If you notice blue or green urine without an obvious dietary or medication-related cause, seek medical advice. Although rare, infections or genetic conditions could be the underlying cause.
9. Cloudy or Murky
What It Means: Possible urinary tract infection (UTI), kidney stones, or dehydration.
Explanation: Cloudy urine often indicates an infection, particularly UTIs, where bacteria or white blood cells can cause a cloudy appearance. High levels of certain minerals or crystals in the urine, which can lead to kidney stones, can also cause cloudiness.
Caution: Cloudy urine accompanied by a foul odor, burning sensation, pain, or frequent urge to urinate is often a sign of a UTI, which should be treated promptly to prevent infection from reaching the kidneys.
Additional Tips for Monitoring Urine Color and Kidney Health
1. Hydrate Wisely: Aim to drink 6-8 glasses of water daily, but remember that individual needs vary based on climate, physical activity, and health conditions.
2. Be Mindful of Dietary Influences: Foods like beets, carrots, and certain berries can alter urine color temporarily. Keep track of your diet if you notice changes.
3. Monitor for Consistency: Occasional variations in urine color are usually harmless, but persistent changes, especially with additional symptoms, should be evaluated.
4. Know Your Medications: Many medications and supplements can affect urine color. If you’re taking something new, ask your pharmacist about side effects.
5. Consult a Professional for Persistent Changes: Regular checkups and discussions about urine color, especially with a history of kidney issues, can help catch potential problems early.
Conclusion
ADVERTISEMENT